
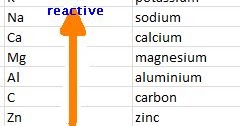
It appears to embody both thermodynamic factors and kinetic factors-i.e., whether or not a substance reacts, and how fast it reacts. Reactivity is a somewhat vague concept in chemistry. The term reactivity is related to the concepts of chemical stability and chemical compatibility.
Equilibrium point of the reaction (i.e., the extent to which all of it reacts). Variety of substances with which it reacts. The chemical reactivity of a substance can refer to the variety of circumstances (conditions that include temperature, pressure, presence of catalysts) in which it reacts, in combination with the: Interacts with two or more other reactants to form two or more products. Forms new substances by addition of atoms from another reactant or reactants. The chemical reactivity of a single substance (reactant) covers its behavior in which it: theories to predict and to account for these processes. experimental methods that are used to observe these processes. methodology that applies to the study of reactivity of chemicals of all kinds,. the systematic study of sets of reactions of these two kinds,. the chemical reactions of two or more substances that interact with each other,. the chemical reactions of a single substance,. 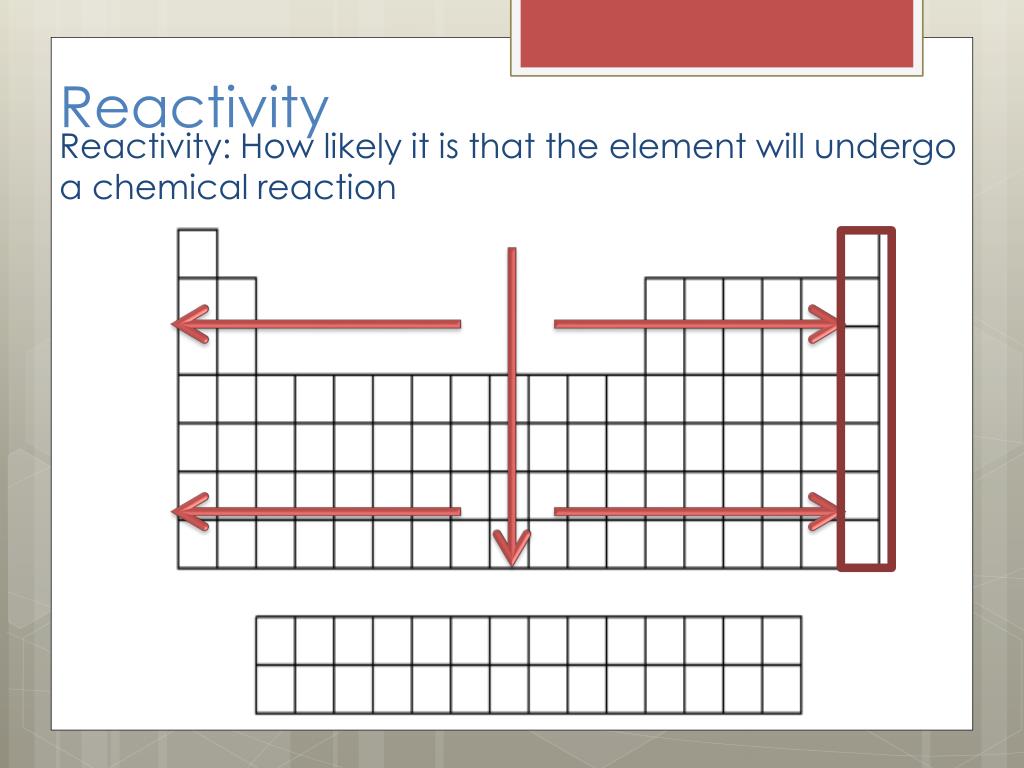
In chemistry, reactivity is the impulse for which a chemical substance undergoes a chemical reaction, either by itself or with other materials, with an overall release of energy.
JSTOR ( June 2016) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.įind sources: "Reactivity" chemistry – news Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. This article needs additional citations for verification.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
